Ganglion Impar Block
Performed by the award winning doctors in Raleigh, North Carolina
Ganglion Impar Blocks are generally non-to minimally invasive and are conservative in nature.
Use the form on the right to request a call from our Patient Concierge Group.
Give us a call today at (919) 787-7246.[/color-box]
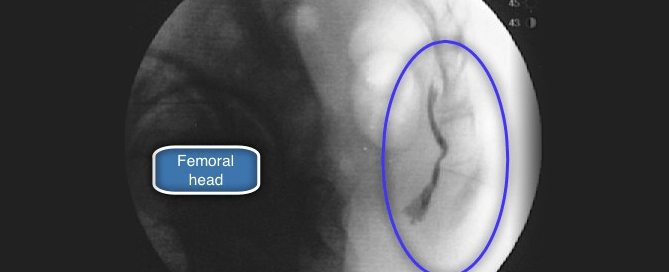
How is a Ganglion Impar Block Performed?
The first documented use of the ganglion impar block was in 1990. Since that time, the procedure has been modified to enhance its effectiveness and make it more comfortable for the patient. Doctors can choose from several different approaches to the ganglion block procedure. Examples of the different techniques for ganglion impar blocks include:
- Transoccygeal joint approach
- Paramedical approach
- Paracoccygeal corkscrew approach
- Transsacrococcygeal approach
Although there are several methods of ganglion impar blocks, the transsacrococcygeal approach is the most widely used due to its effectiveness and simplicity.
Conditions Related To Ganglion Impar Block
The causes of sympathetic nervous system pain are complex. Chronic perineal pain (CPP) in the ganglion impar region could be caused by a wide variety of factors. Vascular pain is frequently associated with causes such as poor blood supply to the nerves. Visceral pain could be caused by chronic pancreatitis, some non-malignant pelvic pain syndromes, upper abdominal cancer, rectal cancer, and chronic perineal cancer.
Other conditions that may cause perineal pain include failed back surgery syndrome, spinal cord malformations, and sacral postherpetic neuralgia. In some cases, perineal area pain may be caused by a secondary underlying condition, such as a urinary tract infection, sexually transmitted disease, or prostate inflammation. Consult with your primary physician to eliminate one of these other potential causes before considering a ganglion impar block.
The ganglion impar block can be beneficial for pain stemming from several organs, which include the following:
- Perineum
- Distal third vagina
- Anus
- Distal rectum
- Vulva
- Scrotum