Post-Laminectomy Syndrome Treatment
Performed by the award winning doctors in Raleigh, North Carolina
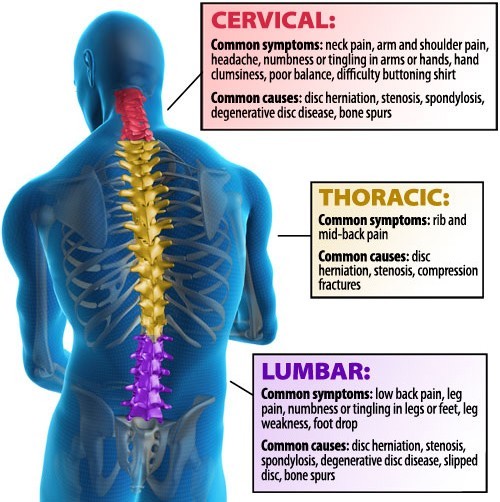
Post-laminectomy syndrome refers to cervical, or lumbar, pain with an unknown cause that can persist despite attempting surgical intervention or that emerges following surgery. This condition is associated in particular with back surgery, which is also known as a laminectomy. Post-laminectomy syndrome is also frequently referred to as failed back surgery syndrome.
The back is comprised of a complex network of bones, muscles, and other tissues that span from the neck to the pelvic bone. The spinal column is a bony structure that acts as the body’s support and protects the delicate spinal cord and associated nerve roots. The spinal column is positioned such that the individual bones of the spine, or the vertebrae, link together creating flexible support. Inside of this column the spinal cord descends down from the brain. In a typical adult, the spinal cord reaches to just below the rib cage.
Treatments for Post-Laminectomy Syndrome are generally non-to minimally invasive and are conservative in nature.
Use the form on the right to request a call from our Patient Concierge Group.
Give us a call today at (919) 787-7246.[/color-box]
Causes of Post-Laminectomy Syndrome
Existing literature on post-laminectomy syndrome is varied. It is not known what causes back pain to persist following surgery. In general, it is believed that the formation of scar tissue after surgery can compress nerve roots within the surrounding area, and this is what likely explains the persistent pain.
Other widely accepted explanations for this condition include:
- Surgical intervention performed at the wrong spinal level
- Lamina that was not removed completely
- Inflammation within the protective layers of the spinal cord
- Other factors that affect recovery from surgery, such as depression
Treatment for Post-Laminectomy Syndrome
Given that the underlying cause of post-laminectomy syndrome is generally unknown, the condition can be quite difficult to treat. It is best to discuss your condition with your physician so as to determine the best available pain management treatment plan.
Over-the-counter pain relievers may be beneficial in providing relief from pain. A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) is believed to help patients who are experiencing moderate pain. These medications are recommended because of their ability to reduce inflammation and thereby reduce the associated pain. There are a number of medications that were originally developed to alleviate symptoms of depression that have also been shown to be effective for relieving pain. Oral corticosteroids, such as prednisone and cortisone, may also be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation of the affected area.
Individuals, whose pain does not respond to over-the-counter remedies, may wish to speak to their doctor about prescribing codeine to help manage their pain. Codeine is an opioid medication whose pain-relieving effects arise by binding to the opioid receptors within the brain. Studies have provided support for the use of opioids in short-term relief of sudden-onset, severe pain; however, concerns related to the misuse and abuse of this medication suggest that long-term use of opioids for managing pain is contraindicated.