Intro
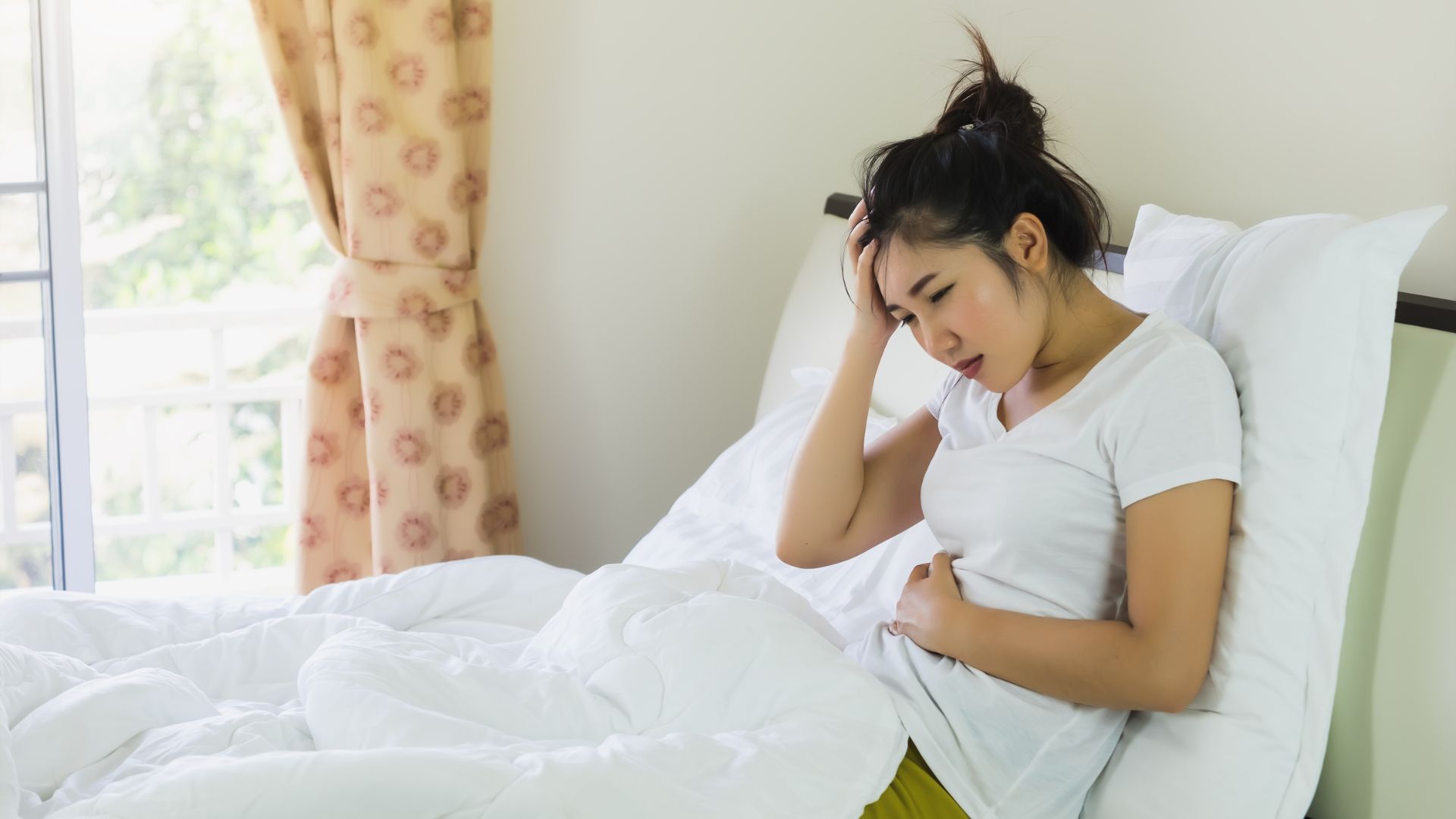
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) is a debilitating condition that is often misunderstood and misdiagnosed. Its symptoms can be overwhelming and its impact can be far-reaching. This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of this complex condition. We will delve into the symptoms, causes, and available treatments, offering insight and guidance for those living with CRPS.
Understanding What Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Is
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, or CRPS, is a chronic pain disorder that usually targets a single limb and often develops after an injury. What distinguishes CRPS is the intensity of the pain, which generally seems out of sync with the severity of the original injury. Researchers believe that CRPS stems from a disruption or malfunction in the peripheral and central nervous systems. While the syndrome can affect anyone, it appears to favor certain demographics. People between the ages of 20 and 35 have a higher likelihood of developing CRPS, and women are three times more likely to be diagnosed than men. For a more comprehensive insight into CRPS, the [National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/All-Disorders/Complex-Regional-Pain-Syndrome-CRPS-Information-Page offers valuable information on their page dedicated to this complex condition.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
One of the primary identifiers of CRPS is its prolonged, severe pain that seems disproportionate to the initial injury. It typically targets a single limb, with the pain often described as a burning sensation or as if a vice is being tightened around the affected area. Beyond pain, CRPS also triggers changes in the skin, often resulting in variations in color and temperature. You may notice the skin on the affected limb turning blue, red, or purple and it could feel unusually warm or cool to touch. Swelling is another common symptom. Over time, the affected area may also experience increased sensitivity to touch or cold, muscle spasms, joint stiffness, and decreased mobility, making daily activities increasingly difficult. It’s important to note that the range and severity of these symptoms can vary from person to person.
Identifying the Causes and Risk Factors
The precise root of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome remains a mystery, despite frequent association with an injury, surgery, or serious health events such as a stroke or heart attack. Yet, it’s important to note that not everyone experiencing these events will develop CRPS, which suggests additional factors at play, potentially including genetic predisposition. Our understanding of CRPS continues to grow, but the ambiguity surrounding its causes means there’s no certain way to predict its onset. Additionally, some studies suggest a possible link between the development of CRPS and psychological factors, though this connection remains a subject of ongoing debate in the medical community. Unraveling the complexities of CRPS and its causes can be perplexing, but by deepening our understanding, we can move closer to more effective prevention strategies. If you’re curious to know more about the potential triggers and risk factors associated with CRPS, the Mayo Clinic’s dedicated CRPS page is an excellent resource.
How Complex Regional Pain Syndrome is Diagnosed
Navigating the pathway to a CRPS diagnosis can be somewhat tricky, primarily due to the absence of a definitive, single test for this condition. The diagnosis journey typically starts with a detailed review of your medical history, followed by a comprehensive physical examination. The hallmark of CRPS – persistent, severe, and unexplained pain – serves as a critical diagnostic clue. Imaging tests, including X-rays, MRIs, and bone scans, often come into play, helping doctors gain a clearer picture of the situation and rule out other potential causes of the pain. Such tests can also provide insights into changes in bone and tissue, typically seen in later stages of the condition. It’s important to bear in mind that while these diagnostic tools can assist in forming a diagnosis, they do not guarantee a certain answer. However, the more you know, the better equipped you are to navigate this process. If you’re looking for more insights into the diagnostic process for CRPS, our comprehensive Diagnosis and Tests serves as a valuable resource.
Available Treatment Options for CRPS
While a cure for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome remains elusive, numerous treatments can significantly reduce its symptoms, making daily living more manageable. Medication is often the first line of defense, with over-the-counter pain relievers, antidepressants, corticosteroids, and opioids potentially providing some relief. Physical therapy can be instrumental in maintaining and improving limb mobility and strength while reducing pain levels. Another key facet is psychological therapy, offering techniques to manage the emotional aspects of living with chronic pain.
In instances where symptoms are particularly severe or unresponsive to other treatments, more invasive measures may be considered. These could include nerve blocks, which can provide temporary pain relief, or more permanent solutions such as spinal cord stimulation. This procedure involves implanting a device under your skin to send electrical signals to your spinal cord, helping to mask pain signals.
These treatment options are not one-size-fits-all and what works for one person may not work for another. It’s important to have an open dialogue with your healthcare provider to determine the most effective treatment strategy for your specific circumstances. For an in-depth look at these and other potential treatment options, be sure to visit our Treatment for CRPS Coping Mechanisms and Support
Managing life with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) can be taxing both physically and psychologically. Therefore, adopting effective coping strategies is crucial for mitigating stress and fostering resilience. Consider relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga which may help soothe the nervous system, reducing pain intensity. Regular physical activity, customized to your abilities and pain level, can improve mobility, strength, and overall wellness.
Beyond physical strategies, emotional support plays a vital role in coping with chronic pain. Connect with others who are experiencing similar challenges through a support group. Sharing experiences and exchanging coping strategies can offer relief, understanding, and encouragement in a way that your regular social circle may not be able to.
Additionally, partnering with mental health professionals can empower you with the tools to navigate the emotional turbulence that often accompanies chronic pain. They can provide you with strategies to manage feelings of frustration, anxiety, depression, or isolation that might come up.
For a comprehensive list of resources and support groups catering specifically to those living with CRPS, visit the RSDSA’s resources page. Remember, living with CRPS can be challenging, but with the right coping mechanisms and a strong support system, you can cultivate resilience and maintain a good quality of life.
Final Thoughts on Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
Navigating the complexities of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome is undeniably challenging, but gaining a deeper understanding can be a game changer. Prompt medical attention and intervention can halt the progression of the condition and alleviate its symptoms. Incorporating lifestyle adaptations and leveraging available resources can also enhance your ability to cope with the day-to-day challenges of CRPS. Keep in mind that the road to managing CRPS is not a one-size-fits-all journey; it requires a tailored approach that considers your unique situation. Be proactive in seeking treatment options and stay open to trying various coping strategies until you find what works best for you. Lastly, remember that while living with CRPS may feel isolating, you’re not in this alone. We at Wake Spine & Pain are here to provide professional guidance, compassionate care, and effective treatment strategies. Together, we can work towards improving your quality of life and empowering you to thrive despite CRPS.